Problem
The iris data set consists of the physical parameters of three species of flower — Versicolor, Setosa and Virginica. The numeric parameters which the dataset contains are Sepal width, Sepal length, Petal width and Petal length. In this data we will be predicting the classes of the flowers based on these parameters.The data consists of continuous numeric values which describe the dimensions of the respective features.
Every machine learning project begins by understanding what the data and drawing the objectives. While applying machine learning algorithms to your data set, you are understanding, building and analyzing the data as to get the end result. Following are the steps involved in creating a well-defined ML project:
- Understand and define the problem
- Prepare the data
- Explore and Analyse the data
- Apply the algorithms
- Reduce the errors
- Predict the result
Classification with Scikit-Learn
Loading Required Library
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
Loading Iris data
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
df.head()
x = df.iloc[:,0:4]
y = df.iloc[:,4:5].values.ravel() # flatten the numpy array
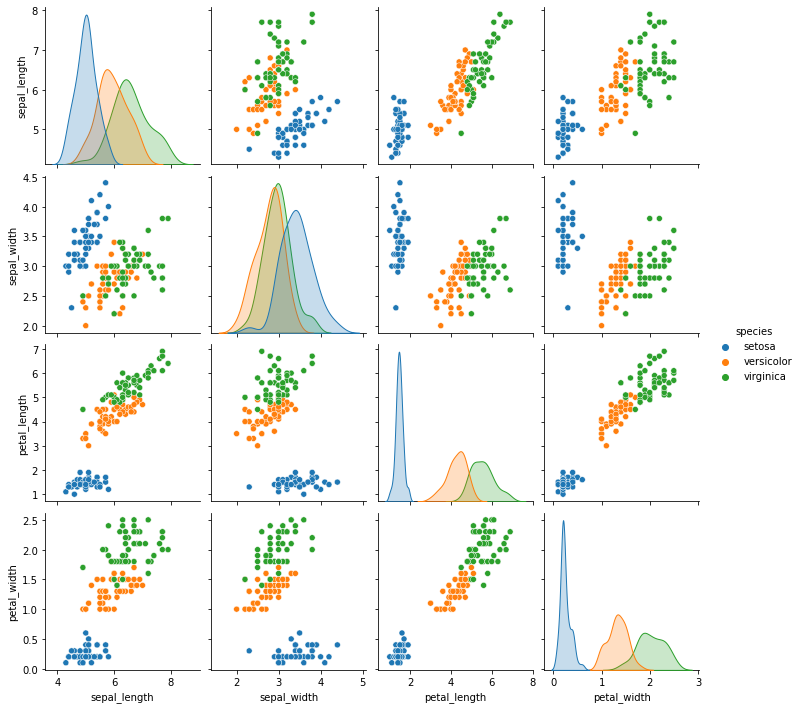
Exploratory Analysis
sns.pairplot(data=df, hue='species')
Building model
models = []
models.append(('Logistic Regression',LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000)))
models.append(('Naive Bayes',GaussianNB()))
models.append(('Decision Tree',DecisionTreeClassifier()))
models.append(('KNN',KNeighborsClassifier()))
models.append(('SVM',SVC()))
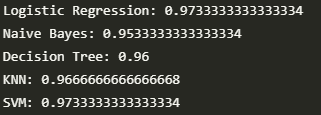
for name, model in models:
result = cross_val_score(model,x,y,cv=10,verbose=0)
print(f'{name}: {result.mean()}')
Classification with Tensorflow
Loading required library
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
Loading iris data and apply one hot encoding
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
x = df.iloc[:,0:4].values
y = df[['species']]
encoder = OneHotEncoder()
y = encoder.fit_transform(y).toarray()
Define DNN model
We need to encode species categoriy value using one hot encoding for feeeding Artificial Neural Network. One Hot Encoding is a common way of preprocessing categorical features for machine learning models. This type of encoding creates a new binary feature for each possible category and assigns a value of 1 to the feature of each sample that corresponds to its original category
def model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(8,input_dim=4, activation='tanh'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='tanh'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='tanh'))
model.add(Dense(3, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy",optimizer="adam",metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
estimator = KerasClassifier(
build_fn=model,
epochs=200, batch_size=20,
verbose=0)
results = cross_val_score(estimator, x, y, cv=10)
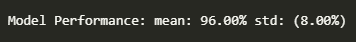
print("Model Performance: mean: %.2f%% std: (%.2f%%)" % (results.mean()*100, results.std()*100))\